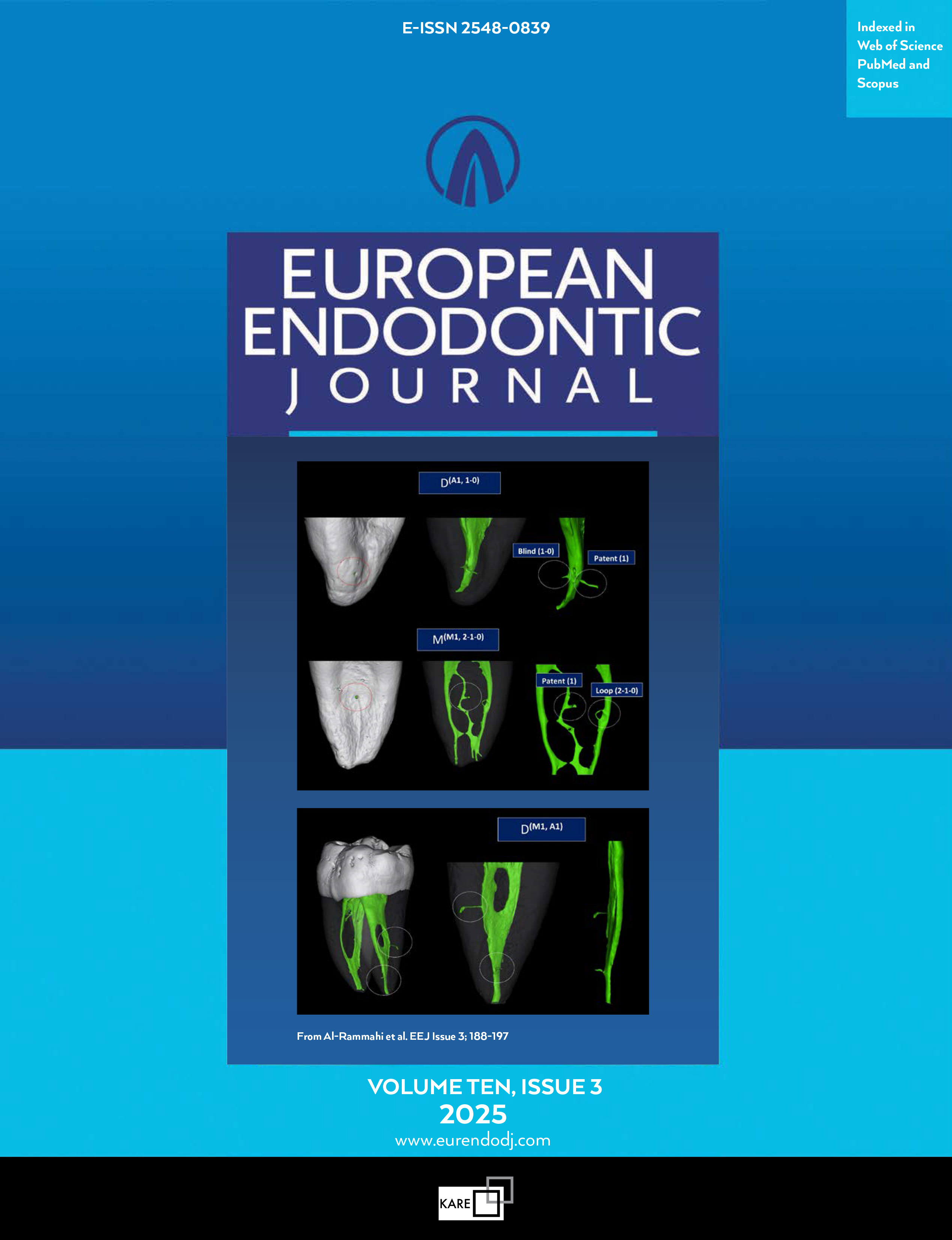
Metrics
2024 IMPACT FACTOR
5 year Impact Factor
Eigenfactor Score
2024 CiteScore
Journal Citation Reports
(Clarivate 2025, JIF Rank)
Advanced Electrochemical Reamer (EC-Reamer) for Root Canal Treatment
Remya Ampadi Ramachandran1, Wei Li2, Shweta Khande1, Ahish Shylendra3, Amit Ranjan Trivedi3, Qian Xie4, Christine Wu2, Mathew Thoppil Mathew51Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, USA2Department of Pediatric Dentistry, College of Dentistry, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, USA
3Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, USA
4Department of Endodontics, College of Dentistry, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, USA
5Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, USA; Department of Restorative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, USA
Objective: According to the American Association of Endodontists (AAE), 22 million endodontic procedures have been performed annually. Root canal treatment is needed to prevent infection and restore function when a tooth is severely infected or decayed. This procedure is the only way to preserve the natural tooth and avoid artificial replacement (implant, denture, etc.). The current study aims to develop an electrochemical reamer (EC-Reamer or EC-R) that can help to disinfect the canal system and thus improve the success rate of root canal treatment.
Methods: The COMSOL Multiphysics software was utilized to simulate the experimental setup and confirm the current flow in the electrolyte. The benchtop experimental approach follows a specific electrochemical protocol, (i) open circuit potential to monitor the electrochemical stabilization and (ii) potentiostatic scan at 9.0 V as the treatment stage. Identification of feasible reference electrode (RE) and insulation material for the exploratory benchtop studies considered platinum (Pt) and gold (Au) wire as the REs and hot melt adhesive (HMA) and liquid tape as the insulation materials. The antimicrobial effects of EC-R were analysed using Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis). One-way ANOVA with the Tukey post hoc test and a significance level of P<0.05 is used to compare the groups with an experimental duration of 60 seconds.
Results: The findings showed that magnitude and current fluctuations created by Pt wire are promising when compared to Au wire, while PtHMA pair is chosen considering Pt's good electrochemical inertness and HMA's easy handling, availability, and non-hazardous features. The use of potentiostatic duration of 1 s and 3 s resulted in >99.99% E. faecalis reduction. Duration at 5 s and above resulted in a total bacterial kill. Statistical analysis confirmed a significant difference among the groups tested with commercial and custom-built potentiostats.
Conclusion: The outcome provided preliminary data for developing an EC-R prototype to enhance the antimicrobial effect during root canal treatment potentially. (EEJ-2022-01-04)
Manuscript Language: English
(685 downloaded)