Metrics
2024 IMPACT FACTOR
5 year Impact Factor
Eigenfactor Score
2024 CiteScore
Journal Citation Reports
(Clarivate 2025, JIF Rank)
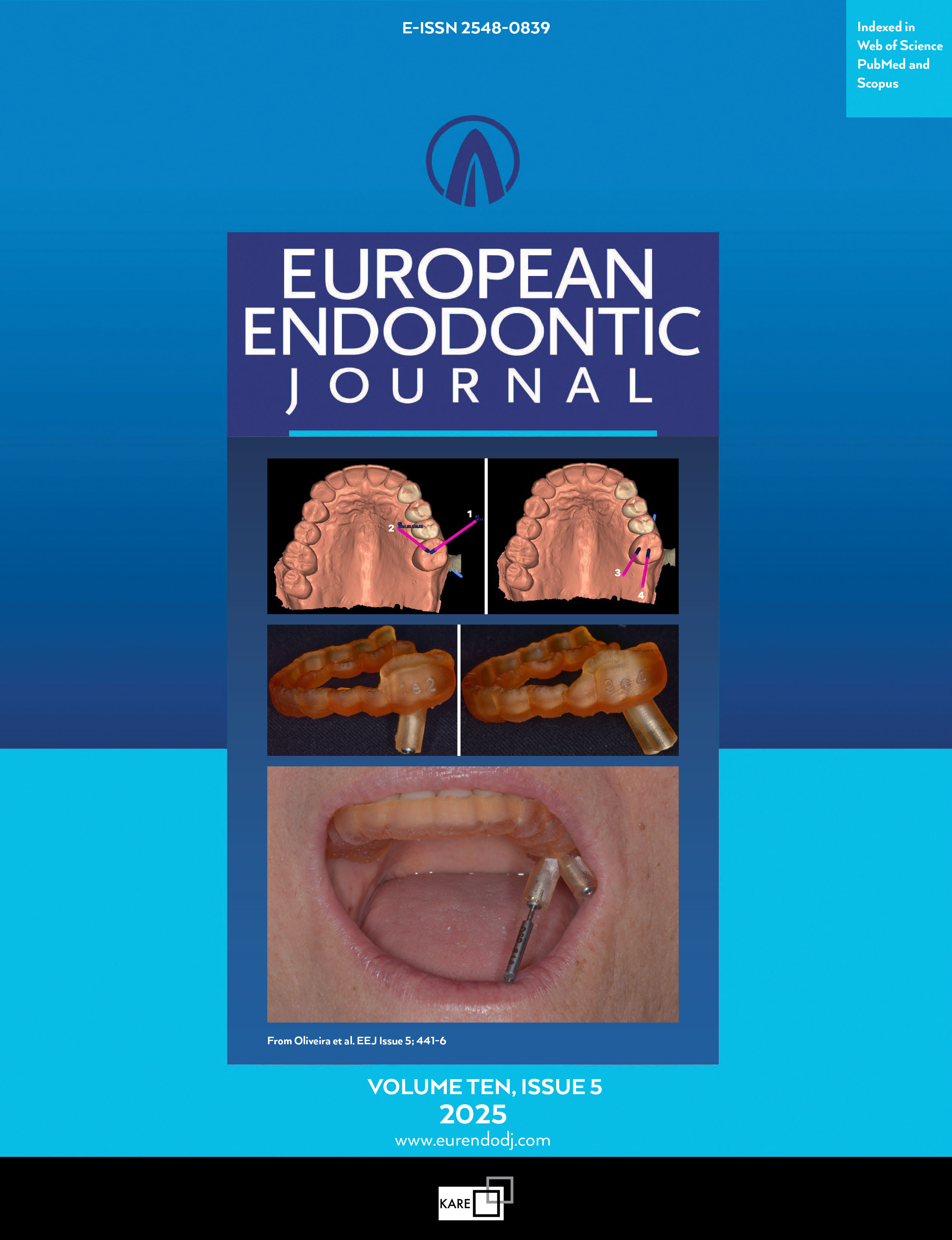
Antimicrobial Efficacy of Calcium Hydroxide Nanoparticles Combined with Nisin Against Enterococcus faecalis in Root Canal Infections
Atia Nurul Sidiqa1, Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria3, I Made Joni2, Ani Melani Maskoen4, Arief Cahyanto31Department of Dental Materials, Faculty of Dentistry, Universitas Jenderal Achmad Yani, Cimahi, Indonesia2Department of Physics, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Universitas Padjadjaran, Sumedang, Indonesia; Functional Nano Powder University Center of Excellence, Universitas Padjadjaran, Sumedang, Indonesia
3Department of Clinical Sciences, College of Dentistry, Ajman University, Ajman, United Arab Emirates
4Department of Oral Biology, Faculty of Dentistry, Universitas Jenderal Achmad Yani, Cimahi, Indonesia
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the antimicrobial effects of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) nanoparticles combined with nisin against Enterococcus faecalis in infected root canals.
Methods: The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC50) and Fractional Inhibitory Concentration (FIC) index were determined to assess the potential synergistic effect of the combination. Root canal specimens infected with E. faecalis were divided into three treatment groups: Ca(OH)2 nanoparticles with nisin, Ca(OH)2 nanoparticles alone, and a control group with no treatment. Colony Forming Units (CFU) were quantified at different dentinal depths, and the relative gene expression of E. faecalis was analysed using quantitative PCR.
Result: MIC50 was not achieved by Ca(OH)2, while nisin had an MIC of 50 mg/mL. FIC analysis indicated no synergistic interaction between Ca(OH)2 and nisin. From the root canal specimen model, Ca(OH)2 nanoparticles alone and the combination of Ca(OH)2 nanoparticles and nisin disinfected dentinal tubules up to 1.3 mm, however, neither group achieved disinfection at a depth of 1.5 mm. Relative gene expression analysis showed that the combination treatment significantly reduced E. faecalis gene expression compared to Ca(OH)2 alone.
Conclusions: The combination of Ca(OH)2 nanoparticles and nisin does not improve the antimicrobial activity of Ca(OH)2 nanoparticles against E. faecalis, suggesting independent antimicrobial activity of both agents. (EEJ-2025-04-054)
Manuscript Language: English