Metrics
2024 IMPACT FACTOR
5 year Impact Factor
Eigenfactor Score
2024 CiteScore
Journal Citation Reports
(Clarivate 2025, JIF Rank)
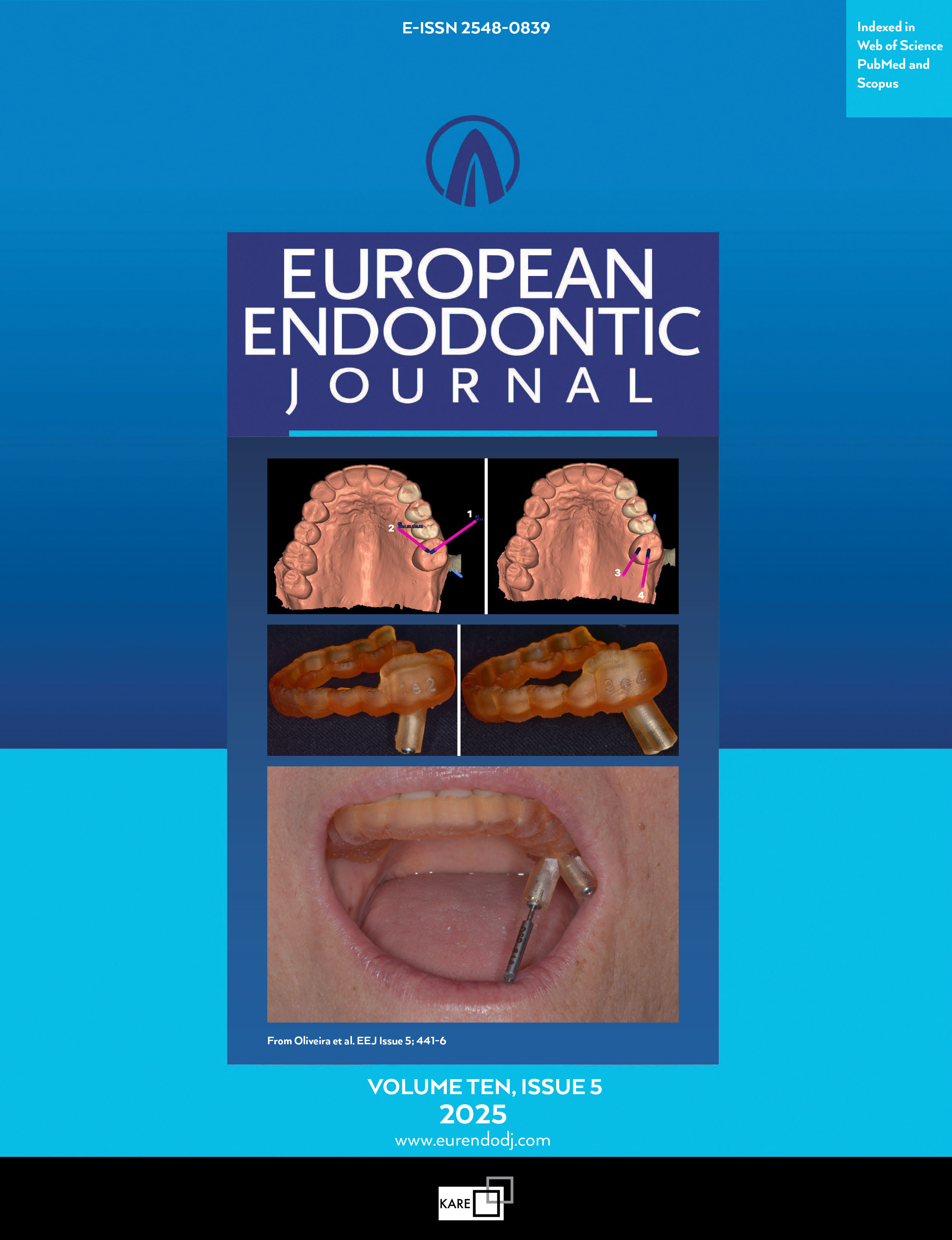
Effect of Final Irrigation Solutions on Mechanical Properties of Root Canal Dentine
Diatri Nari Ratih1, Andina Widyastuti1, Asteria Monika21Department of Conservative Dentistry, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Faculty of Dentistry, Yogyakarta, Indonesia2Conservative Dentistry Specialist Study Program, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Faculty of Dentistry, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Objective: The final irrigation solution should have the capability of a chelation agent to remove the smear layer. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), novel silver citrate, and chitosan nanoparticles as a final irrigation solution on the mechanical properties of root canal dentine, namely the flexural strength and elastic modulus.
Methods: Thirty-two intact, single, and straight roots, with no caries, no cracks, and no restoration of premolars, were assigned into four groups of 8 teeth each. Group 1: irrigated with EDTA; Group 2: irrigated with novel silver citrate; Group 3: irrigated with chitosan nanoparticles; Group 4: irrigated with saline as control. Using a Universal Testing Machine, each sample was tested for flexural strength and elastic modulus with a three-point bend test. The data were analysed using one-way ANOVA and followed by the Tukeys test with a significance level of 0.05 (p=0.05).
Results: Chitosan nanoparticles generated the highest flexural strength and elastic modulus of root canal dentine (212.03±1.64 and 16.40±1.05, respectively) than EDTA (127.10±0.90 and 7.37±0.94) and novel silver citrate (177.87±2.03, and 12.27±1.01) (p<0.05). However, chitosan nanoparticles have similar flexural strength and elastic modulus of root canal dentine when compared to saline (213.76±1.48, 17.02±1.14, respectively) (p>0.05).
Conclusion: Among final irrigations used, chitosan nanoparticles produced the highest flexural strength and elastic modulus of root canal dentine compared to EDTA and novel silver citrate. (EEJ-2024-02-035)
Manuscript Language: English
(643 downloaded)