Metrics
2024 IMPACT FACTOR
5 year Impact Factor
Eigenfactor Score
2024 CiteScore
Journal Citation Reports
(Clarivate 2025, JIF Rank)
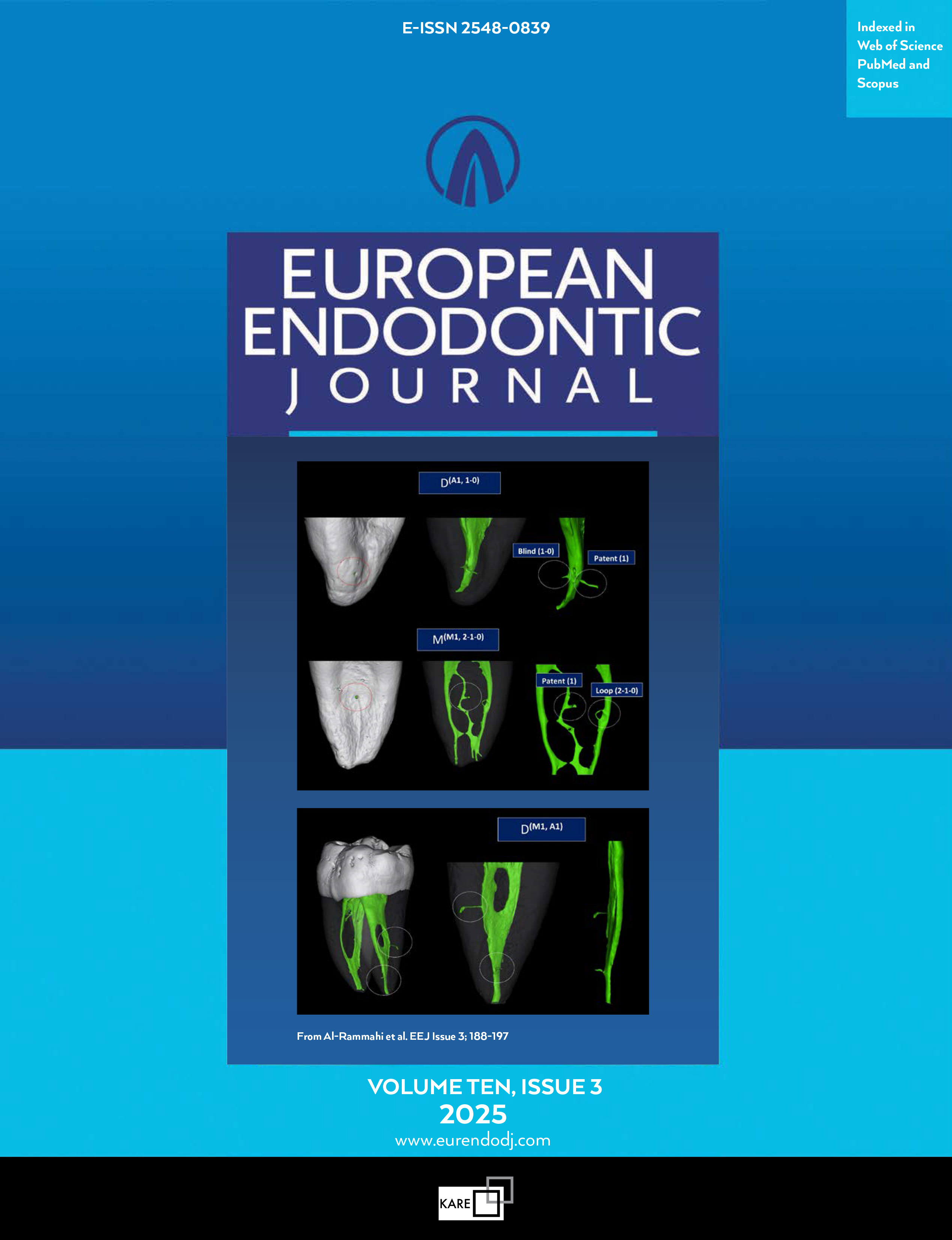
Effect of Intraligamentary Tramadol Hydrochloride on Anesthetic Success During Endodontic Management of Mandibular Molars: A Randomized Clinical Controlled Trial
Vivek Aggarwal1, Mamta Singla2, Alpa Gupta3, Umesh Kumar4, Masoud Saatchi51Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Jamia Millia Islamia, Faculty of Dentistry, New Delhi, India2Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, SGT Dental College, Haryana, India
3Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Manav Rachna Dental College, Faridabaad, India
4Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Chandigarh, India
5Department of Endodontics, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Faculty of Dentistry, Isfahan, Iran
Objective: Tramadol hydrochloride has shown local anesthetic properties similar to lidocaine, apart from a central analgesic effect. The present study evaluated the effect of the administration of tramadol alone or in addition to 2% lidocaine, as supplementary intraligamentary injections.
Methods: One hundred and five patients, with a failed primary inferior alveolar nerve block (IANB), were randomly allocated to one of the three supplementary intraligamentary groups: 2% lidocaine with 1: 80,000 epinephrine; tramadol hydrochloride (50 mg/mL); and 2% lidocaine with 1: 80,000 epinephrine plus tramadol hydrochloride. Patients received 1.2 mL doses (0.6 mL of each root). Patients reporting pain ≤54 on Heft Parker visual analogue scale (Heft-Parker VAS), were categorized as successful anesthesia. A finger pulse oximeter was used to measure the heart rates. The anesthetic success rates, gender, and type of tooth were compared using the Pearson chi-square test. The heart rates and age were statistically evaluated using the one-way analysis of variance test. The level of significance was set at 0.05 (p=0.05).
Results: The initial IANB was successful in 31% of cases. There were significant differences in the anesthetic success rates of different supplementary intraligamentary injections (χ2= 33.6, p<0.001, df=2). The 2% lidocaine-plus-tramadol resulted in significantly higher success rates than the two groups. There were no significant changes in the baseline heart rates of all groups (p>0.05).
Conclusion: The addition of tramadol to 2% lidocaine with 1: 80,000 epinephrine, given as supplementary intraligamentary injection, can help in achieving successful anesthesia during the endodontic management of mandibular molars with irreversible pulpitis resistant to IANB injections. (EEJ-2023-05-064)
Manuscript Language: English
(846 downloaded)