Metrics
2024 IMPACT FACTOR
5 year Impact Factor
Eigenfactor Score
2024 CiteScore
Journal Citation Reports
(Clarivate 2025, JIF Rank)
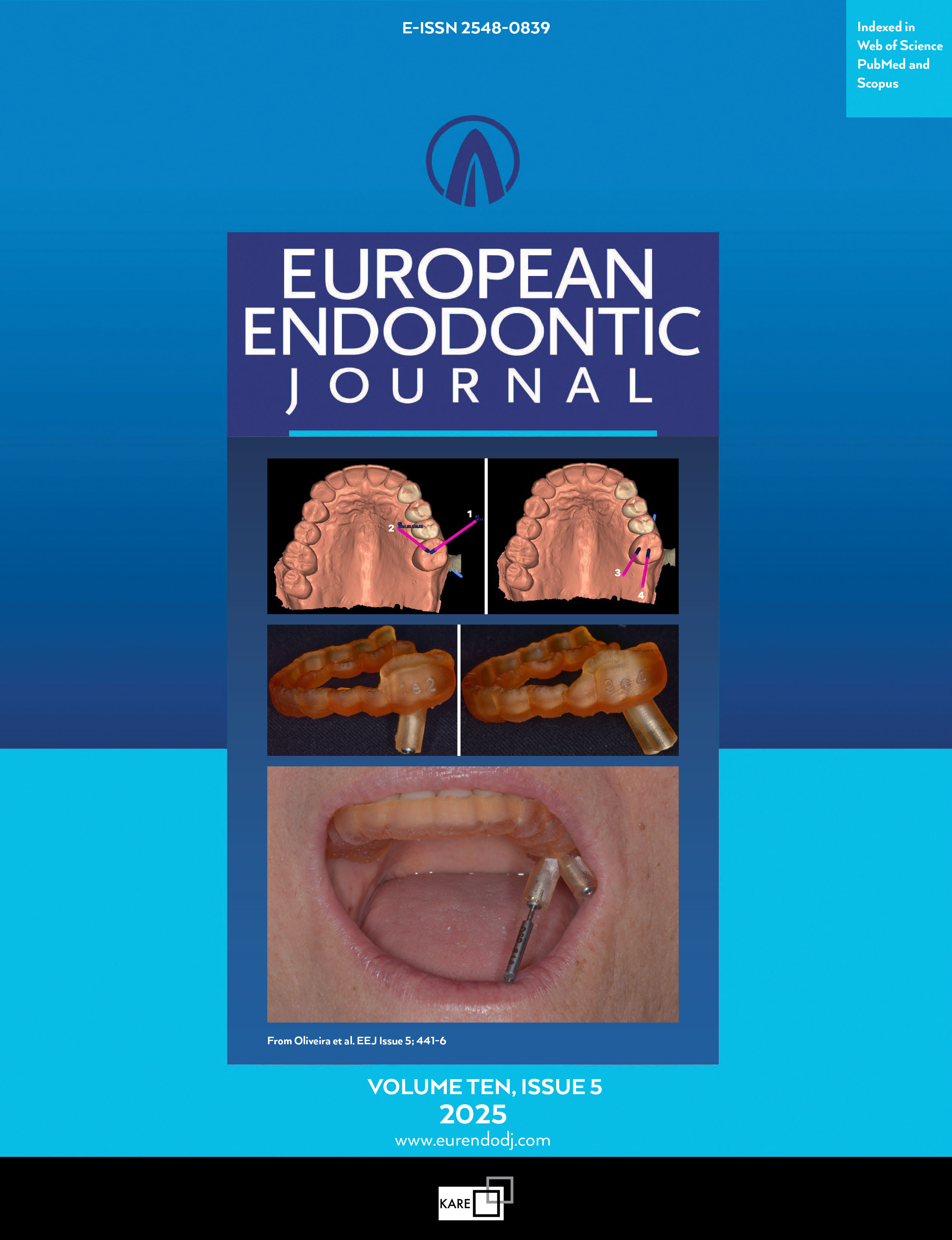
Effectiveness of Laser-activated Irrigation Modalities on Intracanal Bacterial Elimination and Apical Extrusion
Mohamed Marwan Abbas1, Sunaina Shetty Yadadi1, Ashna Sulaiman2, Okba Mahmoud3, Ahmed Jamleh1, Saaid Al Shehadat11Department of Restorative Dentistry, University of Sharjah, College of Dental Medicine, Sharjah, UAE2Research Institute for Medical and Health Sciences, University of Sharjah, Sharjah, UAE
3Department of Clinical Sciences, Ajman University, Faculty of Dentistry, Ajman, UAE
Objective: This study aimed to compare photon-induced photoacoustic streaming (PIPS) and diode laser with passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI) in activating intracanal irrigants for bacterial elimination from the root canal and apical extrusion.
Methods: Sixty extracted single-canal human teeth were chemo-mechanically prepared and placed in 3 ml glass vials with sterile 0.9 % sodium chloride solution. The root canals were inoculated with Enterococcus faecalis and incubated for 24 hours at 37°C. The samples were divided into three experimental groups (PIPS, diode laser, and PUI) and a control group (n=15 each). The experimental groups had root canals filled with saline and activated according to the manufacturers instructions, while the control group received saline without activation. Bacterial samples were collected from the canals and outside the apex for quantification, cultured on nutrient agar for 24 hours at 37°C, and counted as colony-forming units. Mean values were compared using one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni tests at 5 % significance.
Results: All activation protocols significantly eliminated intracanal E. faecalis compared to the negative control group (p<0.05). PUI and the diode lasers were significantly more effective than PIPS (p<0.05). Extruded bacteria were higher in PUI than in PIPS and diode lasers.
Conclusion: Within the limitations of this study, the tested techniques extruded bacteria and did not completely eliminate intracanal bacteria. The diode laser showed the best bacterial elimination and extrusion outcome. (EEJ-2024-07-112)
Manuscript Language: English
(1385 downloaded)