Metrics
2024 IMPACT FACTOR
5 year Impact Factor
Eigenfactor Score
2024 CiteScore
Journal Citation Reports
(Clarivate 2025, JIF Rank)
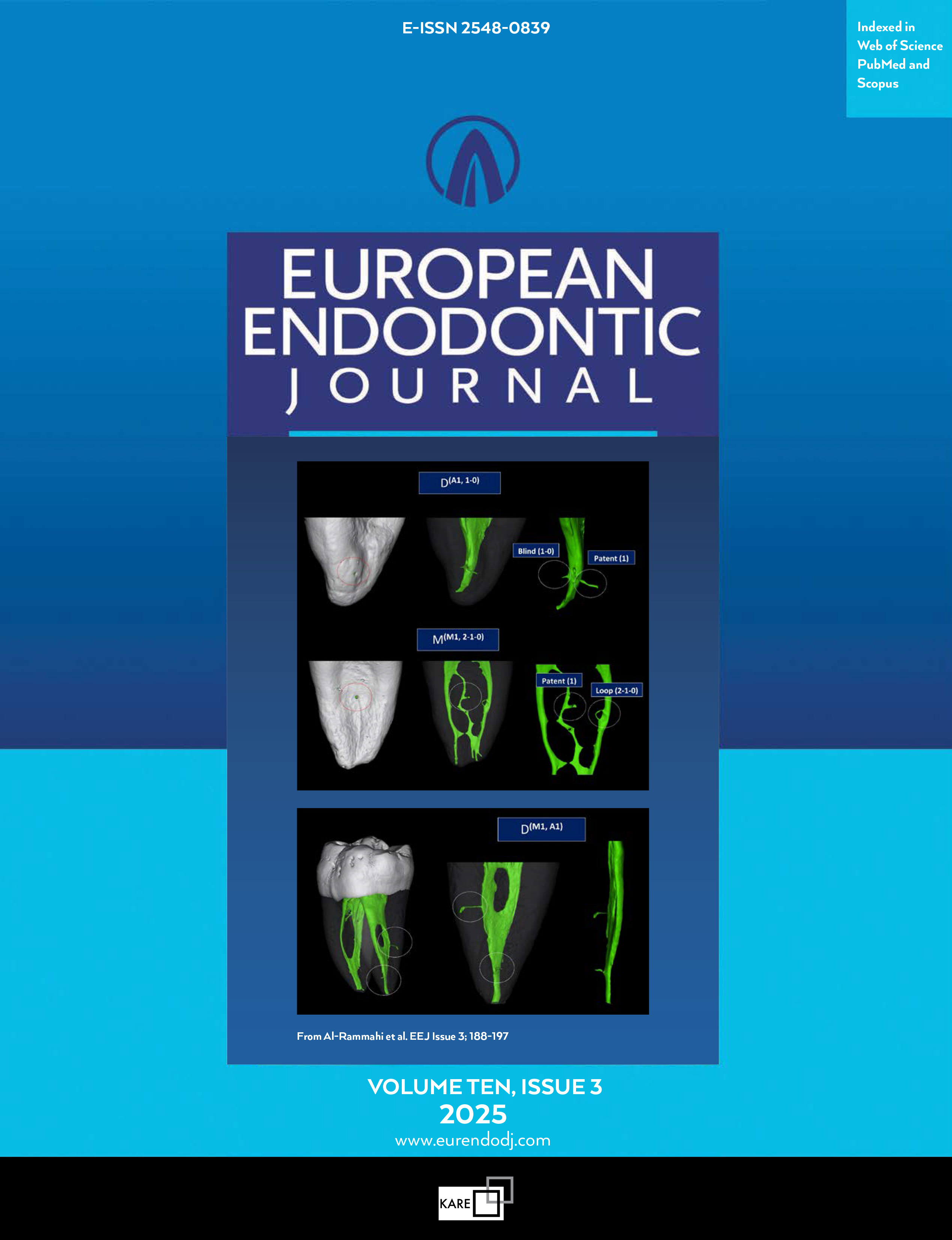
Comparison of the Physicochemical Properties, Antimicrobial Action, and Cytotoxicity of Ambroxol Hydrochloride, N-acetylcysteine, and Calcium Hydroxide Pastes
Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi1, India de Azevedo Queiroz1, Murilo Alcalde2, Sandra Oliveira3, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan1, Paulo Henrique Weckwerth4, Augusto Shoji Kato1, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte11Department of Operative Dentistry, Endodontics and Dental Materials, Bauru School of Dentistry, University of São Paulo, Bauru, SP, Brazil2Department of Dentistry, University Sagrado Coração, Bauru, São Paulo
3Department of Basic Science, Araçatuba Dental School, UNESP, Araçatuba, São Paulo, Brazil
4Department of Mibrobiology, Unimed Hospital, Bauru, São Paulo, Brazil
Objective: To evaluate the solubility, pH, antimicrobial action, and cytotoxicity of ambroxol hydrochloride (AMB), N-acetylcysteine (NAC), and calcium hydroxide (CH) pastes for use as intracanal medications.
Methods: Solubility was determined by micro-CT, based on the paste volume remaining after immersion in water for 7 days. pH was measured by immersing acrylic tubes containing the pastes in ultrapure water and then measuring pH after 3 hours, 3 days, and 7 days. Antimicrobial action against Enterococcus faecalis was assessed based on the percentage of living cells, using the live/dead staining method under confocal microscopy. Cytotoxicity was assessed based on the cell viability of L929 fibroblast-like cells after 6, 24, and 48 hours. Cytotoxicity data were compared using the ANOVA and Tukey tests, and the antimicrobial data were compared using the Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn tests. The significance level used was 5% (α=0.05).
Results: The solubility values for all the study groups were significantly different (P<0.05), where the highest values were for NAC, followed by AMB, and then CH. Likewise, the pH levels were all significantly different (P<0.05), where NAC and AMB levels were acidic, and CH levels were alkaline. The antimicrobial action of AMB was significantly higher than that of CH (P<0.05), and that of NAC was also higher than that of CH, albeit not significantly. AMB and NAC were more cytotoxic than CH, and higher dilutions of CH promoted higher cell viability levels than lower dilutions of the same paste (P<0.05).
Conclusion: : The NAC and AMB pastes were more soluble and cytotoxic than the CH paste and had acidic pH levels. The AMB paste displayed the highest antimicrobial action against Enterococcus faecalis biofilm. (EEJ-2021-12-209)
Manuscript Language: English
(673 downloaded)