Metrics
2024 IMPACT FACTOR
5 year Impact Factor
Eigenfactor Score
2024 CiteScore
Journal Citation Reports
(Clarivate 2025, JIF Rank)
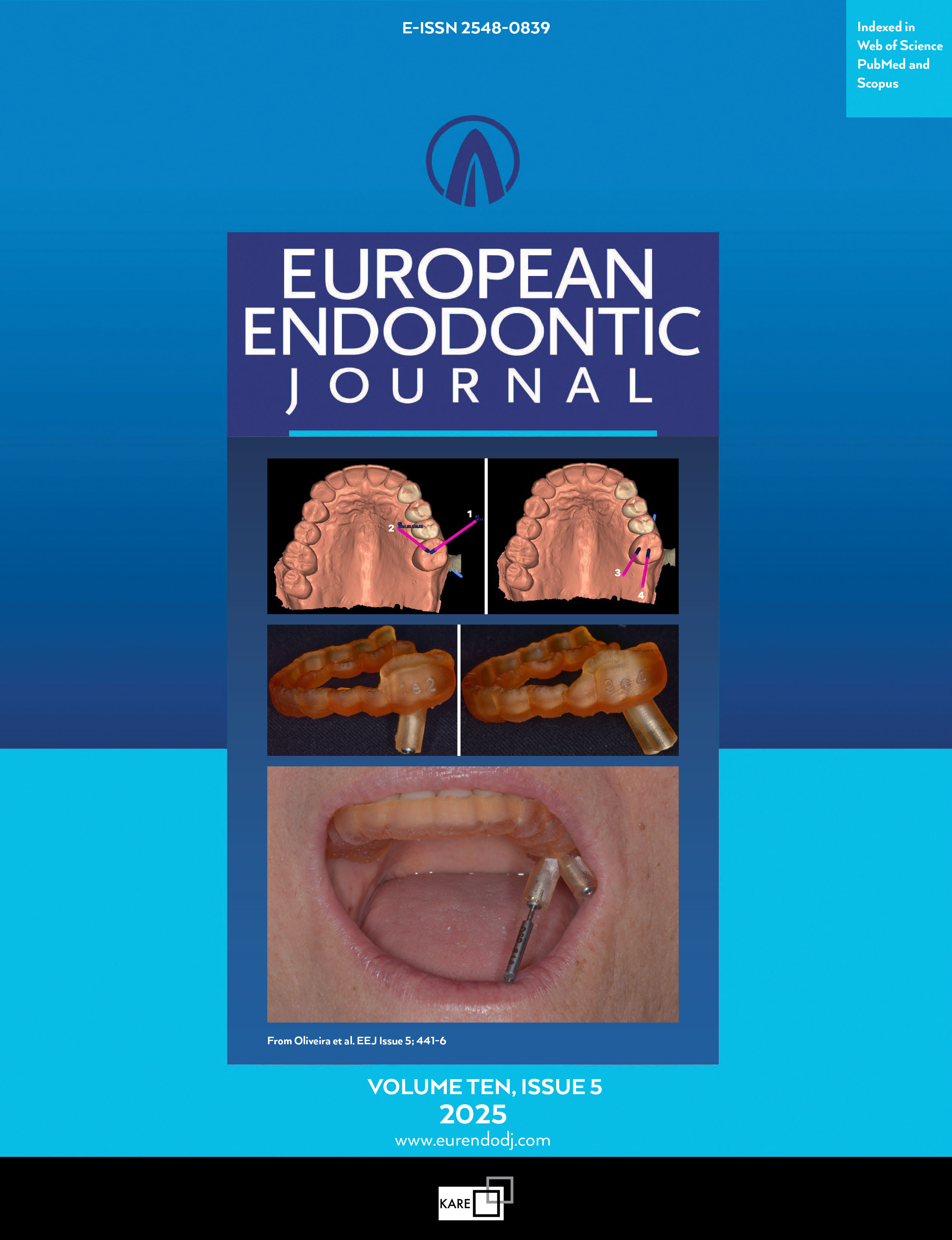
Micro-CT Analysis of Apical Plug Using Various Premixed Bio-ceramic Putties: An In Vitro Study
Alaa M. Eldehna1, Heba Abdelkafy2, Nada A. Salem3, Sherief Elzahar4, Dina M. Abdel Ghany3, Nouralhouda F. Abd Allah1, Dina Yousry El Kharadly3, Mohamed Mohamed Elashiry51Department of Pedodontics and Public Health, Al-Azhar University, Faculty of Dental Medicine for Girls, Cairo, Egypt2Department of Endodontics, Al-Azhar University, Faculty of Dental Medicine for Girls, Cairo, Egypt
3Department of Pediatric Dentistry and Dental Public Health, October 6 University, Faculty of Dentistry, Cairo, Egypt
4Department of Endodontics, Ain Shams University, Faculty of Dentistry, Cairo, Egypt; Private Practice, Istanbul, Türkiye
5Department of Endodontics, Ain Shams University, Faculty of Dentistry, Cairo, Egypt
Objective: Root growth and apical closure continue after tooth eruption. Root growth may cease if pulp viability is lost due to caries or trauma during this period. Successful endodontic treatment is challenging in these cases due to wide root canals and lack of apical stops. New premixed bioceramic root repair putties offer superior handling and healing properties. The aim of this study is to evaluate the filling ability and volumetric changes of three bioceramic putties (BIO-C Repair, NeoMTA Putty, and EndoSequence BC RRM Fast Set Putty) using micro-CT analysis.
Methods: Thirty-six freshly extracted single-rooted teeth with straight root canals were used, divided into three groups based on the materials. Immature teeth were simulated. Pre- and post-obturated micro-CT images were taken for each root. Voids were calculated as the percentage difference between canal space volume and repair material volume. The data were then analysed statistically using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the level of significance set at α=0.05.
Results: All groups showed marginal gaps and/or internal voids after root-end filling. No significant difference between groups in canal and material volumes was detected at 3 mm (p>0.05). However, void percentage differences were significant (p=0.003); Bio-C Repair (9.28±3.27%) and EndoSequence BC RRM (6.7±2.72%) were significantly higher with no difference between them, while NeoMTA Putty (3.73±1.69%) was significantly lower.
Conclusion: NeoMTA Putty exhibited the least volumetric alterations after setting, compared to EndoSequence BC RRM and BIO-C Repair. Enhanced long-term stability as a minimal dimensional change contributes to the material's durability and effectiveness over time, potentially leading to better treatment outcomes making NeoMTA Putty a reliable choice for various endodontic applications, potentially leading to improved success rates and patient outcomes. (EEJ-2024-07-114)
Manuscript Language: English
(578 downloaded)